PRO.MED.CS Praha a. s.
Jsme evropská farmaceutická společnost s vlastním vědecko-výzkumným programem. Naším posláním je převádět nejnovější vědecké poznatky do každodenní lékařské praxe a pomáhat se zlepšováním výsledků léčby a kvality života uváděním moderních, účinných a cenově dostupných léků na trh.
O nás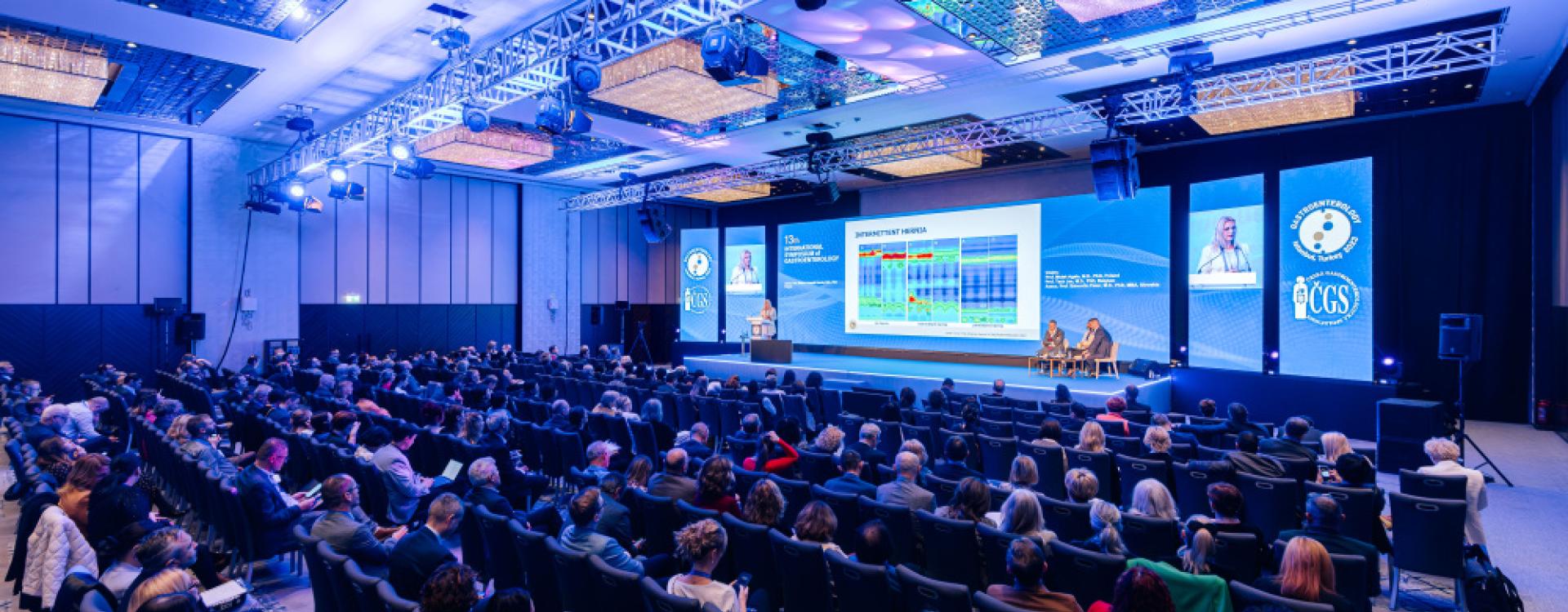
Současné trendy a výzvy v gastroenterologii: ISG 2023
Společnost PRO.MED.CS Praha a. s. měla tu čest být generálním sponzorem 13th International Symposium of Gastroenterology 2023, které se konalo ve dnech 23. až 25. listopadu v tureckém Istanbulu.
Čtěte dále
Naše účast na 50. májových hepatologických dnech 2023
Ve dnech 10. – 12. května 2023 se v Olomouci konal výroční kongres České hepatologické společnosti ČLS JEP, 50. májové hepatologické dny, jehož jsme byli generálním partnerem.
Čtěte dále
Kvalitní a dostupné
léčivé přípravky
Jsme plně integrovaná farmaceutická společnost. Vyvíjíme vlastní lékové formy, vyrábíme léčivé přípravky splňující přísné evropské standardy a interně zajišťujeme vše od předběžných formulací přes stabilitní studie a registrace po celém světě až po design obalů. Staráme se o perfektní fungování celého dodavatelského řetězce, aby se naše léčivé přípravky dostaly vždy tam, kde je jich třeba.
O nás
Péče o lidské zdraví
Naším cílem je pečovat o zdraví lidí a chránit jej. Veškeré úsilí proto soustředíme na vývoj a výrobu vysoce kvalitních léčivých přípravků. Neustále hledáme nová řešení, která přispějí k lepším výsledkům léčby a vyšší kvalitě života lidí celého světa.
Dlouhodobě investujeme do výzkumu a inovací. Podporujeme vědecké týmy a nezávislé laboratoře v hledání nových účinných látek a léčebných postupů.
Široké portfolio
léčivých přípravků
Přípravky z našeho širokého portfolia pomáhají především v léčbě onemocnění gastrointestinálního traktu, ale významně se zaměřujeme také na oblast onemocnění kardiovaskulárního systému a CNS. Náš roční objem produkce tablet, potahovaných tablet a tobolek aktuálně přesahuje miliardu kusů. Všechny naše produkty splňují přísné normy pro výrobu léčivých přípravků ve více než třiceti zemích světa, kde naše společnost působí.
ProduktyAktuální témata

Současné trendy a výzvy v gastroenterologii: ISG 2023
Společnost PRO.MED.CS Praha a. s. měla tu čest být generálním sponzorem 13th International Symposium of Gastroenterology 2023, které se konalo ve dnech 23. až 25. listopadu v tureckém Istanbulu.

Představili jsme novinku na českém trhu: Nový Selzink Plus!
Společnost PRO.MED.CS, která se mimo jiné také specializuje na doplňky stravy, přinesla na český trh exkluzivní novinku. Nový Selzink Plus!

Přinášíme nové a výhodnější balení přípravku YLPIO
PRO.MED.CS z kraje nového roku přinesl na český trh nové balení našeho úspěšného léku YLPIO.
Kariéra
Náš tým průběžně rozšiřujeme o odborníky z různých oblastí. Třeba hledáme právě Vás!
Práce u nás